 |
LanScape VOIP Media Proxy® |
 |
Getting Started |
 |
The LanScape VOIP Media Proxy® |
 |
Media Proxy Configuration |
 |
Configuration Dialogs |
 |
Backing up and restoring configuration information |
 |
Running Multiple Instances |
 |
Running the proxy server as a service |
 |
Deployment Scenarios |
 |
Help File Version |
|
|
Deploying
in the global IP address space
The easiest way to deploy the VOIP Media
Proxy Server® in conjunction with the Centrex Proxy Server® is to co-locate
the media proxy server on a host machine that has a global IP address.
If you deploy your LanScape Centrex Proxy Server® to the global IP address
space, then you must also deploy your LanScape VOIP Media Proxy Server®
in the global IP address space.
When you deploy the servers in the global IP address space, you ensure
that any other machine in your private or global IP network (the internet)
can access your VOIP domain and that full media proxying will take place.
Deploying to the global IP address space also simplifies network administration
seeing that no special firewall or router setups have to be configured.
Note also that is acceptable to locate your Centrex Proxy Server® and
your VOIP Media Proxy Server® in your DMZ if you have one.
The figure below shows a typical global IP address deployment:
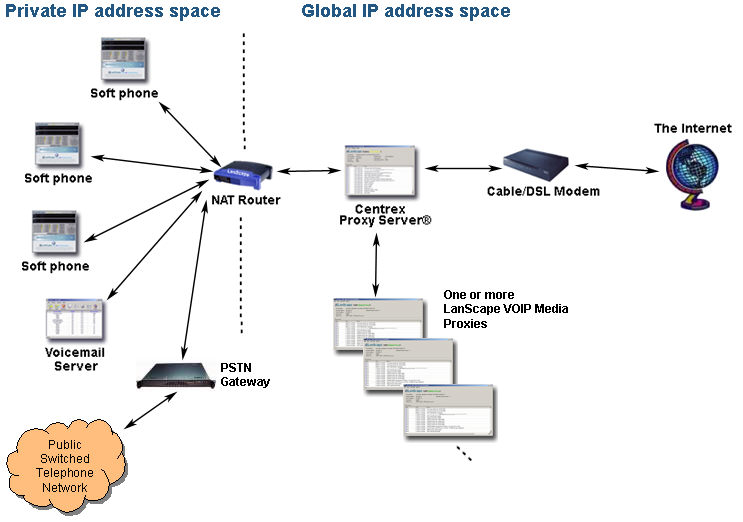
In the above figure, the Centrex Proxy Server® and one or more VOIP Media
Proxy Servers are located outside of the private IP network. The boundary
being the NAT router. The left side of the NAT router represents the private
IP network and the right of the NAT router represents the global IP network.
The figure above shows an internet connection using a broadband cable
or DSL mode. In reality, your connection to the internet can be any technology.
Because the Centrex Proxy Server® and the VOIP Media Proxy Servers are
accessible globally, any soft phone or other VOIP device in the private
network can communicate with the SIP server and have full media proxying
if required. Similarly, any other VOIP domain, single soft phone or other
SIP VOIP device can access the Centrex Proxy Server® thus making calling
into your VOIP domain possible with full media proxying at your private
network boundary if required.
Due to the hostile nature of the current IP4 network regarding peer to
peer VOIP communications, media proxying is recommended for all VOIP deployments.
It allows you to maintain the utmost in private network security while
allowing you to overcome the myriad of issues you must face when deploying
VOIP networks. By deploying one or more LanScape VOIP Media Proxies in
a load sharing configuration, you do not need additional costly network
elements such as session border controllers or boundary controllers. These
additional devices are no longer required which will save you thousands
of dollars during the deployment of your VOIP domain. LanScape
Centrex Proxy Servers will automatically load share with two or more VOIP
Media Proxy servers. Also, any combination of Centrex Proxy Servers and
VOIP Media Proxy Servers can be configured for full media load sharing.
Even if the Centrex Proxy Servers are managing different VOIP domains.
|